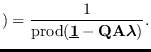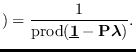The joint MGF of  is, for
is, for
![$=[\lambda_1 \lambda_2 \ldots \lambda_M]^\prime$](img872.png) ,
,
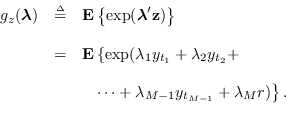 |
(8.10) |
This can be written
where 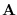 is the
is the 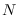 -by-
-by-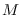 matrix that has 1's everywhere
in the
matrix that has 1's everywhere
in the 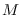 -th column except for 0's in rows
-th column except for 0's in rows
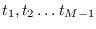 , and
, and 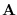 has 1's in row
has 1's in row 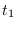 , column 1;
row
, column 1;
row 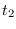 , column 2; etc.
Therefore, from (8.9),
, column 2; etc.
Therefore, from (8.9),
Note that 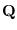 can be a large
can be a large
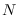 -by-
-by-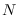 matrix if
matrix if 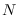 is large. However, if we define
is large. However, if we define
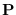 is a reasonable
is a reasonable
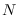 -by-
-by-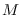 size matrix and can be easily formed directly.
The final simplified form for the joint MGF is
size matrix and can be easily formed directly.
The final simplified form for the joint MGF is