As we mentioned, the mean of vector 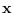 is assumed to be
equal to the degrees of freedom
is assumed to be
equal to the degrees of freedom 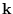 .
If the reference hypothesis
.
If the reference hypothesis 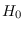 assumes a different
mean value, then we can regard the feature transformation
as having been applied to a scaled variable.
This is easily handled by the change of values theorem.
Let
assumes a different
mean value, then we can regard the feature transformation
as having been applied to a scaled variable.
This is easily handled by the change of values theorem.
Let 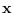 have the prescribed degrees of freedom, but mean
have the prescribed degrees of freedom, but mean
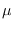 . Then, we write that
. Then, we write that
where
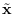 has the standard distribution
with mean
has the standard distribution
with mean 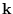 , and
, and
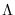 is the diagonal matrix with elements
is the diagonal matrix with elements
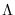
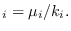 Then, we simply replace matrix
Then, we simply replace matrix 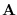 with
with
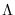
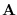 and solve the problem assuming
and solve the problem assuming
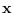 has the standard distribution with mean
has the standard distribution with mean 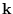 .
.