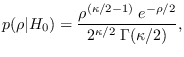The PDF
 can be derived if we
first orthogonalize the features.
Let
can be derived if we
first orthogonalize the features.
Let
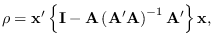 which can also be written
which can also be written
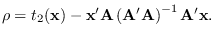 This is the energy in
This is the energy in 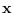 orthogonal to the columns
of
orthogonal to the columns
of 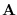 . Accordingly,
. Accordingly, 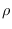 is statistically independent
of
is statistically independent
of 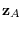 under
under 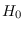 .
Thus,
.
Thus,
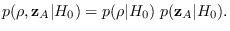 Also,
Also,
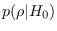 is chi-squared with
is chi-squared with 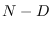 degrees of freedom,
degrees of freedom,
where
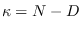 and
and
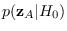 is the Gaussian distribution
with mean
is the Gaussian distribution
with mean 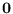 and co-variance
and co-variance
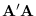 :
:
And, since
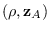 can be obtained from
can be obtained from 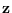 using
a linear transformation with Jacobian of determinant 1,
we can write
using
a linear transformation with Jacobian of determinant 1,
we can write
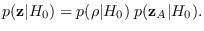 The J-function is just
The J-function is just
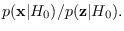 For more information see the function
software/module_lin_gauss.m.
For more information see the function
software/module_lin_gauss.m.